How Telemetry Systems Improve Operational Performance
Published: 1 Dec 2025
Ever wondered how data is collected from remote locations, such as satellites or deep-sea exploration, without direct human interaction? The answer lies in telemetry systems. These systems allow information to be sent back to central systems. How do they work, and what makes them so crucial?
What Are Telemetry Systems?
Telemetry systems are new technologies that enable you to collect and monitor data remotely from multiple sources and devices. These systems continuously send real-time data from sensors or instruments to a central system. This enables quick analysis, accurate understanding, and informed decision-making. Telemetry systems are widely used across fields such as healthcare, aerospace, environmental monitoring, and utilities. They provide useful information that improves performance, streamlines operations, and makes sure that equipment and systems work reliably.
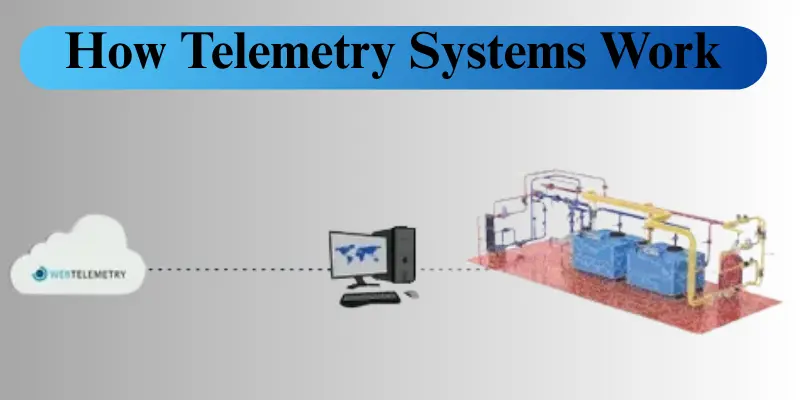
How Telemetry Systems Work
Telemetry systems use sensors or instruments to collect data from remote devices or sources. These sensors measure temperature, pressure, and speed and send the data to a central system in real time. The central system then processes the received data to facilitate exploration. This approach enables individuals to make decisions and monitor operations remotely.
Data Collection: Sensors or instruments gather data from remote sources or devices.
Real-Time Transmission: Data is transmitted to a central system in real time.
Data Processing: The central system processes and analyzes the data.
Remote Monitoring: Enables continuous monitoring of equipment or systems from a distance.
Types of Telemetry Systems
There are many different kinds of telemetry systems, each made to meet the needs of a specific industry. The data they collect, how they send it, and the places they work all affect how these systems work.
- Wired telemetry: transmits sensor data to the central system via physical cables.
- Using radio waves: or other wireless technologies, wireless telemetry transmits data without the need for wires.
- Satellite Telemetry: This technology uses satellites to send data over long distances, often to places that are hard to get to.
- Real-Time Telemetry: Sends live data all the time so that it can be watched and analyzed right away.
- Stored Data Telemetry: This telemetry method stores data locally for later transmission. It’s ideal for places where connectivity isn’t always available.
- Mobile telemetry: sends data over mobile networks, usually for systems that are portable or in vehicles.
- Automatic telemetry: sends data at set intervals, which means less manual data collection is needed.
- Healthcare telemetry: Monitors a patient’s vital signs remotely and transmits the data to healthcare providers, enabling them to closely monitor the patient.
- Environmental telemetry: gathers and sends data from sensors that measure things like pollution and the weather.
- Industrial telemetry: keeps an eye on machines and industrial processes and sends performance data to help with maintenance and operations.
- Aerospace uses telemetry to monitor systems and parts during flight or mission operations.
- Marine telemetry: collects data from sensors on ships or underwater vehicles so that environmental conditions or equipment status can be analyzed in real time.
- Automotive telemetry: keeps track of a car’s performance, such as its speed, fuel levels, and engine status, and sends the data to fleet management.
- Agricultural telemetry: gathers information from sensors or machinery in the field to keep an eye on the health of crops and equipment.
Utility telemetry: keeps an eye on utilities like gas, water, and electricity distribution. It gives managers and operators real-time data to help them run things more smoothly.
The Importance of Telemetry Systems
Telemetry systems are essential in today’s tech-driven world because they let you collect and monitor data in real time from hard-to-reach or remote places. They give businesses constant information about how their equipment and systems are working, which helps them make smart choices, run their operations more smoothly, and avoid expensive failures.
- Remote Monitoring: Enables data collection and system monitoring from remote locations.
- Real-Time Insights: Provides immediate feedback, enabling quick decision-making.
- Predictive Maintenance helps identify potential issues before they become critical.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for manual inspections, saving time and labour costs.
- Improved Performance: Continuously monitors equipment to ensure optimal performance.
- Safety: Identifies hazardous conditions, reduces the risk of accidents, and improves safety.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Provides valuable data to inform operational decisions.
- Minimized Downtime: Detects faults early, allowing for quick interventions and reducing downtime.
- Increased Efficiency: Automates data collection, streamlines operations, and reduces human error.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps meet industry standards by providing accurate, timely data.
- Global Reach: Enables monitoring of systems worldwide, especially in remote areas.
- Environmental Protection: Monitors ecological parameters to prevent damage and ensure sustainability.
- Fleet Management: Tracks the performance and condition of vehicles or machinery remotely.
- Energy Management: Optimizes energy use by monitoring systems such as electrical grids and water networks.
- Innovation: Drives the development of advanced technologies by providing valuable data for improvement.
Core Technologies Behind Telemetry Systems
The core technologies behind telemetry systems are essential for enabling efficient data collection and transmission. These technologies combine sensors, communication networks, and data processing tools to provide real-time insights and remote monitoring across various industries.
Instruments and sensors
Sensors and instruments used to measure and determine temperature, pressure, humidity, and motion form the foundation of telemetry systems. These devices convert physical measurements into electrical signals, which are subsequently transmitted to a central system for further analysis. Sensors must be accurate and reliable for telemetry systems to work well.
Data Acquisition Units (DAQs)
Data Acquisition Units (DAQs) are responsible for acquiring raw sensor data and converting it to a digital format suitable for transmission. To process sensor signals, these units typically include amplifiers, filters, and analogue-to-digital converters (ADCs). DAQ systems ensure data is accurate, reliable, and ready for transmission to a central system or cloud platform.
Networks for communication
Telemetry systems require robust communication networks to transmit data from remote sensors to a central monitoring system. You can connect these networks with wires (like Ethernet or fiber-optic cables) or wirelessly (like Wi-Fi, cellular, or satellite communication). The type of communication technology you use depends on where you are, how much bandwidth you need, and whether you need to send data in real time.
Wireless Transmission Technologies
Telemetry systems can operate without physical cables thanks to wireless technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and cellular networks. These technologies are especially advantageous for tasks such as monitoring the environment, vehicles, or moving machinery from a distance, where running wires would be too laborious or too expensive.
Communication via satellite
Satellite communication is often used for telemetry applications in remote or difficult-to-reach locations. Satellite telemetry sends data from sensors in areas without terrestrial communication networks to geostationary or low-Earth-orbit satellites. Aerospace, marine, and remote environmental monitoring all use this technology a lot.
Storage and computing in the Cloud.
Cloud computing is a key part of telemetry systems because it enables them to store and process data at scale. Telemetry data is sent to cloud servers, where it can be processed, analysed, and stored for later use. Cloud platforms also let you access data from anywhere and provide real-time insights and analytics through web-based dashboards.
Data Processing and Analysis
Telemetry systems rely heavily on data processing and analytics. After the data is gathered, it needs to be processed and analysed to find helpful information. This could mean filtering, combining, and doing statistical analysis. Advanced telemetry systems also use machine learning algorithms to identify patterns, predict when issues will occur, and improve system performance. Such functionality helps people who make decisions act quickly.
Technologies for Security
Security is essential for telemetry systems because they often handle sensitive and vital data. Encryption, authentication, and secure communication protocols safeguard the data during transmission and storage. Access control mechanisms also ensure that only authorised users can access and manage the telemetry data. This prevents unauthorised changes or access to crucial information.
Applications & Use Cases of Telemetry Systems
Telemetry systems can be used across many industries to collect data and monitor systems in real time, helping people make better decisions and work more efficiently. These systems let you track essential parameters from a distance, ensuring safety, performance, and timely intervention when needed in fields like healthcare and aerospace. Telemetry systems are essential tools in many fields due to their wide range of applications.
Monitoring of Health
Telemetry systems are used in healthcare to monitor patients remotely. This allows doctors and nurses to continuously monitor essential signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. These systems help healthcare providers detect early signs that a patient’s condition is worsening, making it easier to act quickly and reducing the risk of readmission to the hospital. Telemetry-based healthcare applications often utilize wearable devices and implantable sensors to transmit real-time data to medical professionals.
Aerospace and aviation
Telemetry systems are critical in aerospace and aviation because they enable real-time monitoring of flight parameters and aircraft systems. These systems track speed, altitude, fuel levels, and engine performance. This information is handy to ground control during flight operations. Telemetry is also very important for space exploration. It is used to monitor the performance of spacecraft and satellites, track environmental conditions, and ensure astronaut safety.
Monitoring the environment
Telemetry is widely utilized for environmental monitoring, especially in remote or perilous areas. It is used to monitor the weather, pollution levels, and water quality. Telemetry systems can monitor pollution sensors in cities, river water temperatures in remote areas, or radiation levels at nuclear plants, for instance. These systems provide real-time information that supports environmental protection and compliance with rules.
Farming and Precision Farming
Agriculture uses telemetry systems for precision farming. These systems use sensors and GPS technology to monitor crop health, soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels. Farmers can use this information to improve irrigation, fertilizer use, and pesticide application, leading to higher crop yields and less environmental harm. Farmers also use telemetry-equipped drones and self-driving cars to map fields and monitor crops.
Managing a fleet of cars
Fleet managers often use telemetry systems to monitor vehicle performance, locate them, and plan optimal routes. Fleet managers can ensure their vehicles are safe and efficient by using these systems to collect data on speed, fuel consumption, tire pressure, and engine performance. Real-time data also helps you determine when maintenance is needed, reducing downtime and extending the life of the fleet.
The Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry uses telemetry systems to monitor drilling operations at remote sites, pipeline integrity, and equipment performance. These systems provide companies with real-time information on pressure, flow rates, and temperature, helping them keep their operations safe and efficient. Telemetry systems are crucial for detecting leaks or problems early, preventing costly breakdowns and environmental damage.
Managing Energy
The energy sector commonly uses telemetry systems to monitor electrical grids, power plants, and renewable energy sources such as solar and wind farms. These systems help improve efficiency, optimize energy distribution, and prevent power outages by continuously monitoring energy production, consumption, and grid stability. Telemetry is also crucial for monitoring how much energy smart homes and buildings use, helping save money and be more environmentally friendly.
Tracking and protecting wildlife
Telemetry systems monitor animal behaviour, health, and movement in wildlife conservation. Collars or tags with GPS can provide information on migration patterns, habitat use, and interactions with other species. This information is beneficial for understanding how ecosystems function, protecting endangered species, and making informed decisions about managing and protecting wildlife.
Automation in manufacturing and industry
Manufacturing uses telemetry to monitor production lines, machines, and tools in real time. Telemetry systems monitor temperature, pressure, vibration, and machine performance. Such monitoring enables predictive maintenance and reduces downtime. Telemetry lets you watch automated systems from afar in industrial automation. Such tracking makes them more efficient and of higher quality, and it reduces the need for people to get involved.
Monitoring of telecommunications and networks
Telemetry systems in telecommunications monitor the health and performance of networks to ensure they run smoothly. These systems gather information about network traffic, signal strength, and bandwidth use. This helps service providers fix problems, improve network performance, and prevent outages. Telemetry systems also monitor the health of telecom equipment such as routers, base stations, and satellites.
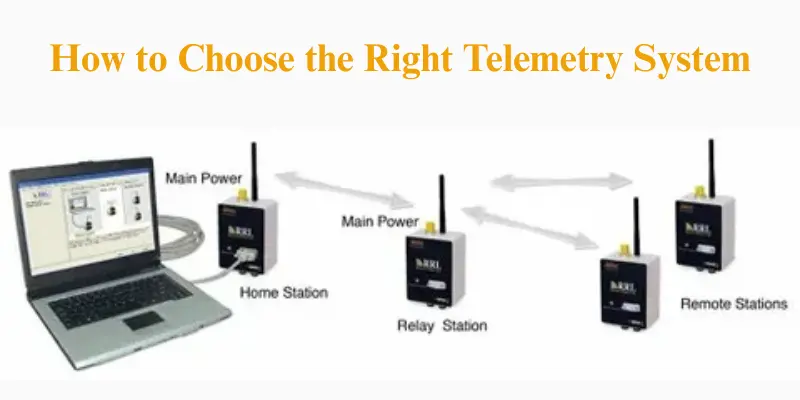
How to Choose the Right Telemetry System
Choosing the right telemetry system is essential because it guarantees efficient data collection, real-time monitoring, and accurate analysis. The selection process involves evaluating factors such as the specific application, data transmission needs, and environmental conditions. Understanding these requirements helps in selecting the best telemetry system that aligns with your operational goals and ensures reliable performance.
Know what you need to apply for.
The first step in choosing the right telemetry system is to figure out exactly what the application needs. Different fields, like healthcare, aerospace, or agriculture, have their own needs for collecting and keeping an eye on data. Knowing what kind of data you need (like temperature, pressure, and speed) and how much detail you need will help you choose the sensors, communication technologies, and data processing tools that will meet those needs.
Consider the specific requirements for sending data.
Consider different ways to send data, such as wired, wireless, or satellite communication, based on the location, coverage area, and bandwidth needs. For example, satellite telemetry may be needed in places where there is no internet access, while Wi-Fi or cellular networks may work better in cities. To get the best performance, make sure the system can send data at the right frequency (real-time, near-real-time, or stored data).
Think about the environment.
Telemetry systems must function effectively in their intended environments. Think about things like extreme temperatures, high humidity, vibration, and contact with dangerous materials that could affect how well the system works. To make sure that sensors and communication equipment last a long time and work well, they need to be tough and weatherproof in harsh conditions.
Flexibility and Scalability
Pick a telemetry system that can grow with your needs. The system should be able to handle more data or more devices without slowing down as your data collection and monitoring needs grow. A flexible system will let you add more sensors, cover more ground, or use new technologies as needed in the future.
Dependability and strength
It’s critical that a telemetry system be reliable, especially in fields where real-time data and system uptime are necessary for safety or efficiency. To avoid losing data during outages or malfunctions, make sure the system has backup systems in place, like battery power for important devices and failover systems for data transmission.
Privacy and Security of Data
Telemetry systems often transmit sensitive information, especially in fields such as finance and healthcare. To keep data private and prevent unauthorised access, the system must include strong security features such as encryption, secure communication protocols, and access controls. It is also essential to follow the data protection rules that apply to you (such as GDPR and HIPAA).
Working with systems that are already in place
Please ensure that your telemetry system is compatible with the software and infrastructure you currently have in place. For quick data analysis and decision-making, it is important that your data sources, cloud platforms, or analytics tools can work with each other. A system that can easily talk to other business systems, like ERP or SCADA, will make operations and data management easier.
Things to think about when it comes to cost and budget
Consider the total cost of ownership, which includes setup, maintenance, and usage. High-end telemetry systems may have more advanced features, but they may also cost a lot of money. Pick a system that offers the best mix of features and cost-effectiveness, balancing your short-term budget constraints with the long-term savings you’ll achieve.
Help and ease of use
A telemetry system that is simple to use is necessary to make sure that operators can properly monitor and analyze the data. Identify systems with dashboards that are easy to use, setup processes that are easy to follow, and configuration options that are easy to understand. Furthermore, ensure that the provider supplies you enough technical support, training, and documentation to help you resolve problems and keep the system running.
Customer Reviews and Vendor Reputation
Please consider researching potential vendors and evaluating their past performance in delivering telemetry solutions. Look for sellers who are known for providing excellent products and great customer service. Customer reviews and testimonials can give you a better idea of how the system works in the real world, which can help you make a smart choice based on what other people have said.
Challenges & Pitfalls in Telemetry Implementations
Implementing telemetry systems can offer significant advantages, but it comes with challenges such as data accuracy, integration issues, and security concerns. Addressing these pitfalls early is crucial for ensuring successful deployment and efficient operation.
Data Accuracy and Calibration
Telemetry systems provide valuable data, but it’s essential to ensure the sensors remain accurate over time. Regular calibration and maintenance can prevent sensor drift and ensure reliable decision-making, especially in critical areas like healthcare and industrial monitoring.
Reliable Data Transmission
For telemetry systems to function effectively, strong and stable data transmission is key. By using advanced technologies and overcoming challenges like signal interference or bandwidth limitations, systems can ensure accurate and timely information, even in remote locations.
Seamless Integration with Existing Systems
While integrating new telemetry systems with legacy infrastructure can be challenging, it offers a valuable opportunity for modernization. With the right expertise and customized development, systems can be smoothly integrated, enhancing overall efficiency and performance.
Managing Costs Effectively
While implementing a telemetry system involves upfront costs, the long-term benefits, such as improved efficiency, predictive maintenance, and reduced downtime, can provide a high return on investment. Careful planning and cost-benefit analysis can help make the system both affordable and sustainable.
Ensuring Data Privacy and Security
Telemetry systems that handle sensitive data must prioritize security. With robust encryption, access control, and monitoring mechanisms, businesses can protect data and maintain compliance with privacy laws, ensuring a secure and reliable system.
Scalability for Future Growth
Choosing a scalable telemetry system ensures it can grow with your business needs. Planning for future expansion from the outset can save costs on upgrades and help the system evolve seamlessly as your data requirements increase.
Efficient Data Management
With the right data management strategies, telemetry systems can efficiently process and organize large volumes of data, providing clear and actionable insights to decision-makers and reducing information overload.
Compliance with Industry Standards
Telemetry systems that operate in regulated industries are equipped to meet the necessary standards for data security, storage, and reporting. This ensures that businesses remain compliant while benefiting from the insights telemetry provides.
Durability in Harsh Environments
Telemetry systems designed for challenging environments, such as extreme temperatures, high humidity, or exposure to chemicals, provide reliable data collection and monitoring. Choosing rugged sensors and equipment ensures the system’s durability and minimizes downtime.
User Training and Adoption
Effective training ensures that users can fully leverage the capabilities of telemetry systems. By providing ongoing support and education, organizations can maximize the value of the system and ensure smooth, efficient operations.

What telemetry systems will look like in the future
The future of telemetry systems looks bright because new technologies are making things that were once impossible possible. These new ideas will simplify data collection, enable real-time monitoring, and enhance the efficiency of many industries. Here are some important trends that will shape the future of telemetry systems:
Working with the Internet of Things (IoT)
Telemetry systems are increasingly added to IoT networks as more and better IoT devices are created. This makes it possible to collect, monitor, and analyze data in more advanced ways, which helps smart cities, homes, and businesses work better. Telemetry systems that use the Internet of Things (IoT) will give us more detailed data, improve automation, and help us make better decisions.
Improvements in wireless communication
Telemetry systems of the future will depend increasingly on 5G and higher for faster and more reliable data transmission. 5G networks will allow real-time monitoring in places that need quick feedback, like self-driving cars, healthcare, and remote industrial operations. This is because they have very low latency and high data throughput.
Putting AI and machine learning together
Telemetry systems that use AI and machine learning (ML) will be able to analyze data and make predictions more intelligently. AI and ML can help automate decision-making by finding patterns and outliers in the data. This lets people take action before problems happen. These developments will make predictive maintenance better, make better use of resources, and make the system work better.
Edge computing for processing data in real time.
Edge computing will be crucial for future telemetry systems because it will process data closer to where it is collected instead of sending it all to a central server. This makes the system more efficient by cutting down on the amount of data that needs to be sent, lowering latency, and making it easier to make decisions in real time.
Better security for data
Cybersecurity will always be a big worry because telemetry systems will be handling more private information. To protect data privacy, integrity, and security, future systems will use advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and blockchain technologies. Improved security measures will prevent data breaches and ensure compliance with global data protection laws.
More systems that work on their own
Autonomous telemetry systems will make operations more self-sufficient. These systems will gather, process, and act on data without any help from people, making monitoring more efficient and real-time. This is especially helpful in fields like agriculture, logistics, and manufacturing, where self-driving systems can cut down on the need for human supervision.
Solutions for the Cloud and Hybrid Cloud
Telemetry systems that run in the cloud will keep getting better, with more storage, analytics, and computing power. Businesses will be able to mix the best parts of private and public clouds with hybrid cloud solutions. This will give them more control, security, and flexibility over their data. This will be very helpful for fields that need to store a lot of data and keep it very safe.
Use of Blockchain to Keep Data Safe
More and more people are using blockchain technology to make sure that telemetry data is safe. Telemetry systems can keep data safe from tampering by using decentralized ledgers. Such an approach makes the data clear and trustworthy. Such systems will be very useful in fields like healthcare, where it is important to keep accurate, unaltered data in order to follow the rules.
Wearable Telemetry Systems
Wearable telemetry systems will get better, especially in the medical field. These devices will continuously monitor vital indicators such as heart rate, oxygen levels, and glucose levels, transmitting the data to healthcare providers in real- time. Wearables will be more comfortable and accurate as sensors get smaller and better. They can also monitor patients’ health remotely.
More use in monitoring the environment
As environmental concerns grow, telemetry systems will increasingly monitor air and water quality, wildlife movement, and climate conditions. These systems will help address environmental problems and support conservation efforts by providing more accurate, up-to-date information from remote and hard-to-reach areas.
Frequently Asked Questions About Telemetry Systems
Explore common questions about telemetry systems and learn how they work in real-world applications.
Telemetry is the remote collection and transmission of data from sensors to a central system for analysis and monitoring.
Sensors measure data, transmit it via communication networks to a central system, where it’s analyzed in real-time.
Calibration ensures sensors provide accurate data, preventing errors in monitoring and decision-making.
Industries like healthcare, aerospace, agriculture, and manufacturing use telemetry for real-time monitoring.
By detecting issues early, telemetry helps prevent accidents and ensures timely interventions to maintain safety.
Wireless telemetry eliminates wiring, offering flexibility and ease of installation, especially in remote areas.
Cloud computing provides scalable storage and processing power for telemetry data, enabling remote access and real-time analysis.
Yes, it can monitor equipment health and predict failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Data accuracy, connectivity issues, integration with existing systems, and data security are common challenges.
Use encryption, secure protocols, and regular updates to protect telemetry data and prevent unauthorized access.
Conclusion
So, guys, in this article, we’ve covered telemetry systems in detail. Telemetry is an essential technology with wide applications in various industries, offering real-time monitoring and valuable insights. Based on the benefits and challenges discussed, I highly recommend integrating a telemetry system tailored to your specific needs, whether for predictive maintenance or remote monitoring. If you’re considering adopting a telemetry system, don’t hesitate to explore the available options and take the next step toward optimizing your operations.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks