Telemetry Data Explained: Insights and Advantages
Published: 4 Dec 2025
Telemetry data involves collecting information from endpoint devices, applications, and systems to monitor their performance, security, and usage. IT teams use this data for real-time monitoring to spot issues before users are affected. By looking at performance insights, organizations can optimize hardware, track network activity, and improve system diagnostics.
Security teams use telemetry to spot unusual behavior, malware activity, and possible threats. In industries such as healthcare and manufacturing, telemetry data helps businesses stay compliant, manage assets, and operate more efficiently. This data is essential for monitoring modern IT infrastructure and making informed decisions.
What Is Telemetry Data?
Telemetry data is information gathered from devices, systems, or applications to monitor their performance. It plays a key role in monitoring endpoints and IT infrastructure, giving organizations complete visibility. Modern telemetry systems collect data from desktops, laptops, mobile devices, and servers, enabling teams to track performance metrics, application usage, and network activity in real time.
For example, a company can collect endpoint telemetry data to see how employees use software on their devices. Ongoing data collection and real-time analysis help spot errors, slowdowns, or unusual activity. With endpoint analytics, IT teams can run system diagnostics and manage devices throughout their lifecycles, ensuring everything remains compliant and runs smoothly.
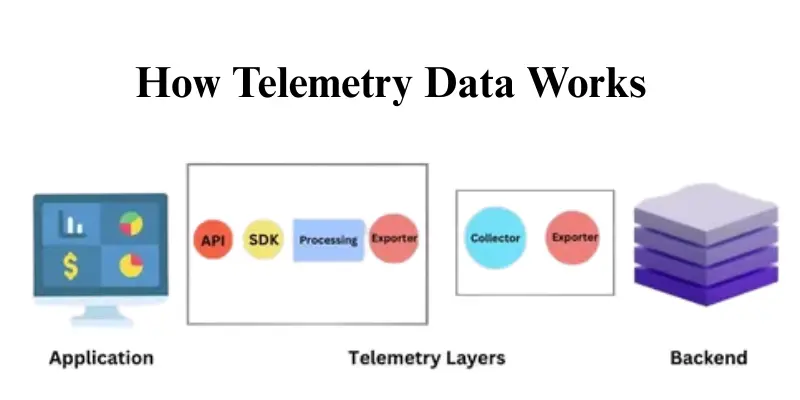
How Telemetry Data Works
Telemetry data is collected by installing agents on devices. These agents gather user activity logs, hardware sensor data, and system logs using tools like Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) or macOS system logs. The raw data is then organized and structured, making it easier to analyze.
- Centralized Data Repository
Telemetry data is stored in a single location, making it easier to manage and access. IT teams can quickly analyze device performance and spot trends. - Cloud-Based Analytics Platform
Data is processed in cloud systems for scalability and advanced analysis. This enables real-time monitoring and insights across all devices. - Real-Time Monitoring
Teams can view system performance and activity as it happens. Immediate detection of issues helps prevent downtime or slowdowns. - Endpoint Performance Insights
Telemetry data shows CPU, memory, and application usage. IT teams use this information to optimize device performance and avoid bottlenecks. - Performance Troubleshooting
Analyzing telemetry helps quickly identify the root cause of problems. This accelerates repairs and reduces the impact on users.
Types of Telemetry Data
Telemetry Data comes in many forms, each valid for specific purposes. System performance metrics track CPU, memory, and storage usage. Application usage monitoring shows which programs are active and how they perform. Security telemetry captures security event logging, malware behavior analysis, and anomaly detection to detect threats early. Network activity tracking provides insight into traffic patterns, IP connections, and bandwidth usage.
Telemetry data comes in different types, each helping organizations monitor devices, improve performance, and enhance security.
User Activity Logs
These logs track how users interact with devices and applications. They record actions like logins, file access, and configuration changes to detect unusual or suspicious behavior.
Endpoint Behavior Analytics
This looks for patterns across devices to improve performance and make sure rules are followed. Industries such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing use it for better security and efficiency.ice Telemetry
IoT devices send data such as temperature, humidity, or machine health. This helps monitor equipment performance and prevent failures in real time.
Proactive Threat Mitigation
Telemetry helps detect potential threats before they escalate. By analyzing device and user activity, IT teams can prevent malware, ransomware, and other intrusions.
Inventory and Asset Management
Telemetry tracks hardware and software across all endpoints. This ensures accurate asset inventory, licensing compliance, and helps IT teams plan maintenance or upgrades effectively.
Telemetry Data Collection Process
Collecting telemetry data is a structured process that ensures devices and applications are monitored effectively. It helps IT teams gather accurate information for performance, security, and compliance.
Goal Setting and Metric Selection
The first stage involves defining objectives for endpoint device monitoring and application performance. Organizations decide which system performance metrics and security telemetry to track.
Deployment of Telemetry Agents
Telemetry agents, or data collection agents, are installed on devices to capture device activity. They collect user activity logs, hardware sensor data, and system logs without affecting device performance.
Data Normalization and Structuring
Raw data is converted into structured telemetry data through data normalization and structuring. This ensures consistent, reliable information across all endpoints and prepares it for analysis.
Data Transmission and Centralized Storage
The processed data is sent to a centralized data repository or cloud-based analytics platform. This enables real-time endpoint analysis, incident response, and threat correlation, providing actionable insights for IT teams.
Telemetry Data Storage and Processing
After collection, telemetry data is stored securely for analysis. Data may be stored in cloud-based analytics platforms, data lakes, or on-premises storage, depending on the company’s needs. Hot storage holds real-time data, while cold storage keeps historical data. IT operations analytics (ITOA) tools process this data to detect performance bottlenecks and monitor endpoint compliance.
Processing can be real-time or batch-based. Structured telemetry data enables teams to perform security monitoring, endpoint protection, and threat detection efficiently. Companies must also comply with regulatory standards (GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA) to protect sensitive data. Maintaining configuration management and asset inventory ensures that devices and applications remain compliant and secure.
Key Features of Modern Telemetry Systems
Modern telemetry systems are designed for real-time monitoring and continuous data collection across many devices. They include features such as automated incident alerts, dashboard visualization, and endpoint behavior anomaly detection. High scalability ensures that even thousands of devices can be monitored without lag.
Advanced systems also integrate with Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and SIEM platform telemetry to enhance security. They support agent-based monitoring, hardware sensors, and network connection logging. By combining endpoint analytics with IT operations analytics, companies can improve operational efficiency and gain actionable insights into endpoint performance.
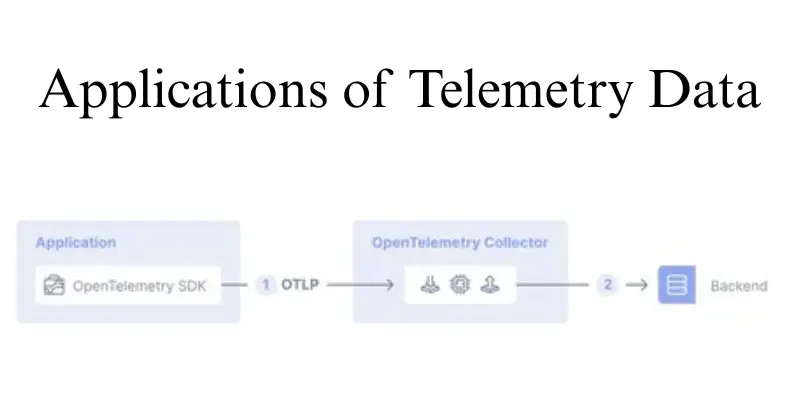
Uses and Applications of Telemetry Data
Telemetry data is used across IT, security, and business operations to monitor devices and improve performance. It helps teams troubleshoot issues, detect threats, and maintain compliance efficiently.
Performance Monitoring Tools
Telemetry helps track system performance metrics, like CPU, memory, and storage usage. IT teams use this data to detect slowdowns and optimize application performance monitoring for smoother operations.
Endpoint Behavior Analytics
Analyzing patterns across devices helps identify unusual activity or inefficiencies. Industries like healthcare and finance rely on endpoint analytics for proactive threat mitigation and operational improvements.
security Telemetry
Security teams use telemetry to monitor malware behavior, conduct analysis, detect anomalies, and identify network threats. This strengthens the organization’s cybersecurity posture and prevents potential attacks.
Threat Correlation
Telemetry data helps correlate events across multiple devices to detect advanced threats. By linking unusual activity with ransomware indicators or APT behaviors, IT teams respond faster.
Inventory and Asset Management
Telemetry tracks hardware and software assets in real time. It ensures accurate asset inventory, compliance with licensing requirements, and a smooth endpoint lifecycle.
Proactive Threat Mitigation
Continuous monitoring allows IT teams to prevent security incidents before they occur. By analyzing user activity logs and device behavior, risks are minimized.
Compliance Monitoring
Telemetry ensures adherence to regulatory standards (GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA). Organizations can produce compliance reporting and verify that all endpoints meet required guidelines.
Benefits of Telemetry Data
Telemetry data offers organizations clear insights into devices, applications, and user behavior. It helps IT and security teams optimize performance, reduce risks, and ensure compliance efficiently.
Real-Time Endpoint Analysis
- Telemetry allows IT teams to monitor devices.
- Problems are detected immediately before they impact users.
- This ensures faster response and smoother operations.
Endpoint Performance Insights
- Data provides details on CPU, memory, and application usage.
- IT teams can quickly identify performance bottlenecks.
- Optimizing systems leads to better application performance.
Security Monitoring and Incident Response
- Telemetry tracks threats, anomalies, and unusual activity.
- Teams can respond to security incidents faster.
- This strengthens the overall cybersecurity posture.
Operational Efficiency Improvements
- Continuous monitoring identifies workflow inefficiencies.
- IT teams save time by troubleshooting proactively.
- Organizations reduce downtime and increase productivity.
Performance Troubleshooting
- Telemetry data helps find the root cause of errors.
- Both software and hardware issues are easier to resolve.
- Quick fixes improve user experience and reduce support costs.
Asset Inventory and Licensing Compliance
- Telemetry tracks hardware and software across endpoints.
- Licensing compliance and asset inventory are maintained accurately.
- This ensures efficiency and adherence to regulatory standards.
Common Challenges in Telemetry Data
Despite its advantages, telemetry data can present challenges. Massive data volumes can overwhelm endpoint analytics systems, making data normalization and structuring critical. Privacy regulations like HIPAA and CCPA add complexity to security telemetry and user activity logs collection.
Other issues include integration across multiple platforms, ensuring configuration management, and avoiding alert fatigue in IT teams. Companies must carefully manage centralized data repositories and optimize IT operations analytics (ITOA) to make sure endpoint protection and threat detection are effective.
How to Get Started with Telemetry Data
Getting started with telemetry data begins by defining clear goals for endpoint device monitoring and continuous data collection. Selecting the right telemetry agents and tools for agent-based tracking is key. Companies should implement secure data transmission, data normalization and structuring, and integrate with cloud-based analytics platforms.
Begin small with a few devices, then scale to cover all endpoints. Use performance monitoring tools, IT operations analytics (ITOA), and security event logging to track improvements. Regularly review endpoint performance insights, application usage monitoring, and network activity tracking to maintain compliance and maximize ROI.
Frequently Asked Questions about Telemetry Data
Telemetry data often raises questions about collection, usage, and security. People want to know how it works, why it matters, and how to implement it safely in modern IT environments.
Telemetry data is information collected from devices, applications, or systems to monitor performance, usage, and security. It helps IT teams track endpoint performance insights in real time.
Data is gathered using telemetry agents installed on devices. These agents capture user activity logs, hardware metrics, and system events without affecting performance.
Telemetry includes system performance metrics, security logs, network activity, and IoT device data. Each type supports performance troubleshooting and operational insights.
Telemetry moves through secure channels using real-time data transfer, encrypted protocols, and centralized storage. This ensures safe data transmission across endpoints.
It helps organizations detect issues early, optimize performance, and prevent security incidents. Telemetry improves operational efficiency and reduces downtime.
Yes, telemetry helps track asset usage, monitor endpoint activity, and produce reports to meet HIPAA, GDPR, and CCPA standards. Asset inventory and licensing compliance are maintained.
Cloud platforms process telemetry for endpoint behavior analytics and threat detection. Teams can gain actionable insights and respond quickly to anomalies.
Conclusion
Telemetry data is essential for modern IT and business operations. Using endpoint telemetry, event logging, and cloud-based analytics, organizations can monitor devices, detect threats, and optimize performance.
Proper collection, secure transmission, and structured analysis ensure systems stay compliant and resilient. Companies that leverage telemetry data effectively gain faster troubleshooting, improved operational efficiency, and stronger cybersecurity, making it a cornerstone of intelligent IT management.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks