Telemetry Data Transmission Techniques: Methods & Best Practices
Published: 4 Dec 2025
Telemetry data transmission techniques enable devices to share important information over long distances in a fast and reliable manner. These techniques guide how sensors, machines, and intelligent systems transmit measurements to servers for analysis. Modern industries depend on clear, steady communication, mainly when operating in complex digital environments.
Many systems rely on real-time data transfer, secure data transmission, network telemetry, cloud-based telemetry, and endpoint telemetry to keep everything running smoothly. As connected devices grow across the USA, strong telemetry methods become even more critical. Good transmission techniques improve system health, boost performance, and create safer operations for industries that need constant insight.
What Are Telemetry Data Transmission Techniques
Telemetry data transmission techniques explain how devices transmit information over long distances in a smooth, reliable manner. These methods help sensors share readings with servers that study them. Many teams in the USA use them to track machines, vehicles, medical tools, and smart devices. Modern systems depend on real-time data transfer, secure data transmission, and network telemetry to stay stable.
- Telemetry data transmission techniques enable devices to send accurate readings to servers without delay, even over long distances.
- Modern systems rely on real-time data transfer and secure data transmission to monitor machines, vehicles, and medical tools safely.
- Engineers use cloud-based telemetry and IoT data transmission to keep information flowing smoothly in smart homes, hospitals, and industrial sites.
Telemetry plays a key role in keeping the USA industries connected and efficient. Strong methods ensure data moves fast, stays secure, and supports better decision-making every day.
History and Evolution of Telemetry Transmission Methods
Telemetry has changed a lot since the early space missions. Engineers once depended on simple analog radios to send rough signals from rockets to ground stations. These early steps proved how powerful long-distance communication could be and set the foundation for today’s advanced systems.
- Digital tools replaced analog systems, delivering clearer signals, higher speeds, and greater reliability.
- Modern systems support smooth telemetry signal transfer across complex networks.
- Cloud platforms improve telemetry data logging and make large datasets easier to analyze.
- Teams rely on telemetry data pipelines and telemetry performance metrics to track system health.
- Secure designs use agent-based telemetry transfer and telemetry agent communication to protect data flow.
Today’s telemetry uses wireless antennas, satellite links, and IP networks to move vast volumes of information. Devices grow smarter each year, and networks become more advanced, enabling more profound insights and safer communication across the USA.
Key Protocols and Transport Mechanisms for Telemetry Data
Telemetry protocols help devices share data quickly, safely, and at the correct cost. Different systems need different speeds and message sizes, so choosing the right protocol matters. Strong designs keep hospitals, power grids, and connected vehicles running without delays.
Lightweight Protocols for Fast Telemetry
MQTT and CoAP work well for small devices that send short messages. They reduce network load and keep sensors active even under weak signal conditions. Many IoT teams in the USA use them for stable real-time updates.
Enterprise-Grade Messaging Protocols
AMQP and HTTP help larger systems move structured data across secure networks. They support tracking tools, dashboards, and analytics platforms. These protocols keep workflows clean when many devices send data together.
Wireless and IoT Transport Mechanisms
Wireless telemetry communication supports mobile sensors in vehicles, farms, and smart homes. It allows data to travel across vast areas without cables. This flexibility helps engineers keep remote devices online.
Data Handling and Normalization Processes
Systems use data normalization in telemetry transfer to remove errors and mismatches. Telemetry log collection keeps records organized for later analysis. This makes it easier to study performance and detect issues early.
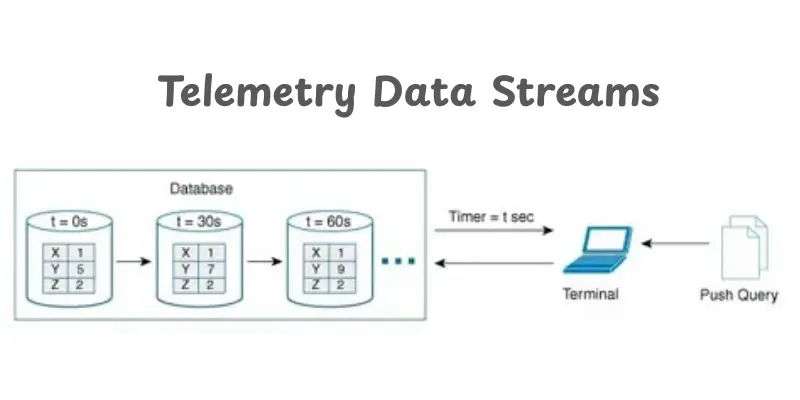
Push vs Pull: Choosing the Right Transmission Mode
Telemetry systems use two main transmission modes to move data smoothly. Push Mode sends updates right away, while Pull Mode waits for a server request. Both work well, and engineers choose based on speed, control, and system needs.
How Push Mode Delivers Instant Data
Push Mode sends telemetry the moment something changes. It supports real-time streaming of endpoint data and fast reactions. Many USA teams use it when systems must stay updated every second.
Why Pull Mode Offers More Control
Pull Mode lets servers decide when to collect data. This works best when timing needs to be exact. It also reduces load when constant updates are not required.
Push Mode Use Cases in Active Systems
Push systems support endpoint device monitoring, transmission, and quick event logging. They help track busy machines that change often. This makes them ideal for networks that handle frequent actions.
Pull Mode Use Cases in Organized Workflows
Pull systems support telemetry system integration and cloud telemetry analytics. They work well for stored data that updates at set times. This helps companies manage large repositories without overload.
Data Formats and Serialization for Telemetry Transmission
Choosing the correct data format is key to smooth telemetry. Formats like JSON, XML, Protobuf, and Avro make sure information moves efficiently. Picking the right one keeps USA systems fast, reliable, and easy to manage.
JSON for Readable Telemetry
JSON is easy to read and widely supported. Engineers use it for simple telemetry data logging and quick testing. It’s perfect when clarity matters more than speed.
Protobuf for High-Speed Systems
Protobuf is compact and parses data quickly. This format supports telemetry data transmission methods and secure data transmission for large-scale networks. It’s ideal for systems handling millions of events per second.
XML for Structured Data
XML works well when devices need a strict structure. It helps organize complex IoT data transmission and ensures messages are consistent. Many older industrial systems still rely on it for compatibility.
Avro for Cloud Pipelines
Avro supports structured telemetry data transfer and telemetry data aggregation in cloud systems. It’s optimized for streaming pipelines and scales easily as new devices join networks. This keeps pipelines fast and stable.
Communication Channels: Wired, Wireless, Cellular, Satellite, and IP Networks
Telemetry uses different channels to move data safely and quickly. Wired, wireless, cellular, satellite, and IP networks all serve unique needs. Choosing the right channel keeps telemetry systems fast, reliable, and secure across the USA.
Wired Channels for Stability
Wired connections provide strong, steady links in factories and critical infrastructure. They support the transfer of telemetry signals and ensure high reliability. Engineers prefer wired networks when downtime is not an option.
Wireless Channels for Flexibility
Wireless telemetry allows sensors to move freely and install easily. It supports wireless telemetry communication and mobile devices. Smart homes, hospitals, and industrial plants benefit from its convenience.
Cellular Networks for Wide Coverage
Cellular links reach remote areas and support smart fleets or outdoor sensors. They help manage network telemetry in large-scale operations. 4G and 5G networks deliver telemetry where wires cannot reach.
Satellite and IP Networks for Advanced Use
Satellite channels cover oceans, deserts, and rural regions. IP networks handle high-speed cloud-based telemetry and massive streams. Combining them ensures robust telemetry data pipelines and smooth system integration.
Ensuring Data security and Privacy During Transmission
Telemetry moves sensitive information that must stay safe during transmission. Teams apply multiple security measures to protect data, and USA regulations guide safe practices.
- Encryption, authentication, and certificate rotation lock data and prevent attackers from accessing it.
- Compliance with HIPAA and NIST guidelines ensures safety in hospitals, aircraft, and industrial systems.
- Strong controls support data encryption for telemetry, secure telemetry communication, and secure data transmission across networks.
- Protections also cover endpoint telemetry, telemetry log collection, telemetry agent communication, and cloud telemetry analytics, where risks are higher.
- Engineers monitor telemetry performance metrics and logs to detect anomalies early and keep systems resilient.
These steps ensure telemetry systems remain safe, reliable, and ready for critical operations.
Handling High-Frequency and Large-Scale Telemetry Data Streams
Some telemetry systems must handle thousands of events every second. High-speed devices create constant pressure on networks and storage. Teams use compression, batching, and filtering to manage heavy workloads. Cloud tools help process massive streams and support stable data streaming techniques across large sensor grids in the USA.
High-frequency data requires innovative telemetry data pipelines, real-time data transfer, high-frequency telemetry updates, and telemetry data aggregation to reduce delays. Edge devices process data near the source to cut network costs. Smart tuning keeps operations running smoothly as systems expand. Strong planning prevents bottlenecks during peak loads.
Integration with Analytics Platforms and Cloud-Based Backends
Telemetry today depends heavily on cloud platforms to store, manage, and analyze data efficiently. USA companies like Boeing and GE use AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to process millions of telemetry events every day. These platforms enable cloud-based telemetry, integration with telemetry systems, and centralized data repository transmission, ensuring large networks stay organized. Dashboards help teams spot problems quickly before they affect operations.
Using Telemetry for Predictive Maintenance
For example, airlines track engine sensors using cloud platforms. Telemetry performance metrics and network monitoring detect early signs of wear, preventing costly failures. Engineers rely on telemetry event logging to plan maintenance on time.
Smart Factories and IoT Analytics
Smart factories use IoT telemetry data flow to watch machines in real time. Endpoint device monitoring transmission allows managers to adjust processes instantly. Data streams from hundreds of sensors feed cloud dashboards for fast, actionable insights.
Healthcare Monitoring Example
Hospitals use cloud-based telemetry analytics to monitor patient devices such as heart rate monitors. Alerts generated from aggregated telemetry data let nurses respond immediately. This integration keeps patient care fast, precise, and safe.
Benefits of Smooth Integration
Smooth telemetry integration ensures fewer delays and accurate insights. Combining telemetry systems integration, cloud-based telemetry, and advanced analytics helps USA companies make informed decisions, reduce downtime, and improve operational efficiency.
Best Practices for Implementation and Performance Optimization
Effective telemetry design begins with clear goals and strong network planning. Engineers choose protocols, formats, and channels that match expected workloads. They also monitor delays, device health, and bandwidth to keep pipelines stable. Wise choices support telemetry data transmission methods, telemetry agent data push, and structured telemetry data transfer, ensuring they run smoothly for years.
Teams also track telemetry performance metrics, aggregate telemetry data, and use OS-level telemetry APIs to spot weaknesses early. Cloud monitoring tools help find slow devices and improve endpoint data synchronization and telemetry data logging. Good practice keeps systems secure and ready for future growth.
Frequently Asked Questions about Telemetry Data Transmission Techniques
People often have questions about how telemetry works, its security, and the best methods for sending data. Here are answers to the most common queries:
Telemetry data transmission is the process of sending measurements from sensors to servers. It ensures real-time data transfer for monitoring systems.
Protocols like MQTT, AMQP, HTTP, and CoAP are widely used. They enable telemetry network protocols and wireless telemetry communication.
Push sends data automatically when events occur, while pull requests data from the server. Both are used for endpoint telemetry.
Data is encrypted, authenticated, and monitored. This supports secure telemetry communication and data encryption for telemetry.
JSON, Protobuf, XML, and Avro are common. Protobuf is ideal for high-frequency telemetry updates and fast processing.
Yes, wireless telemetry and cellular links allow mobility. They are widely used in IoT and remote monitoring.
Telemetry feeds cloud platforms like AWS and Azure. This enables cloud-based telemetry and integration with telemetry systems for real-time insights.
Conclusion
Telemetry data transmission techniques are the backbone of modern monitoring systems. Using real-time data transfer, secure telemetry communication, and cloud-based telemetry, USA industries can track devices, optimize operations, and prevent failures efficiently.
Choosing the proper protocols, formats, and channels ensures fast, reliable, and safe data flow. Proper integration with analytics platforms, combined with strong security and performance monitoring, keeps systems resilient and ready for the future. Strong telemetry pipelines empower smart infrastructure, healthcare, aviation, and industrial operations to make informed decisions every day.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks