Wireless Telemetry: Uses, Benefits, and Applications
Published: 4 Dec 2025
In today’s fast-paced industries, wireless telemetry has become a game-changer for efficiently monitoring and controlling operations. By enabling wireless data monitoring, businesses can track machinery, environmental conditions, and remote assets in real time without physical connections. Industrial wireless telemetry allows factories, energy grids, and transportation networks to operate seamlessly while reducing downtime and errors.
Telemetry devices collect critical information from sensors and transmit it through telemetry communication networks, ensuring managers receive accurate data instantly. With wireless IoT telemetry, companies can integrate data from multiple sources, make faster decisions, and optimise processes. This technology is reshaping how modern industries stay connected and competitive.

What Is Wireless Telemetry and Why Does It Matter Today?
Wireless telemetry is the process of transmitting data from sensors or machines to a central system without using wires. Wireless telemetry applications let companies monitor operations remotely. This is crucial in industries where physical access is difficult or dangerous. Digital telemetry systems provide accurate readings and reduce human error. With wireless machine monitoring, businesses can detect issues before they become serious problems.
Wireless telemetry also improves safety and efficiency. Remote asset tracking telemetry ensures that vehicles, machines, or equipment are operating correctly. Wireless environmental monitoring helps detect hazards or changing conditions. Companies use cellular telemetry systems and wireless automation monitoring to maintain control, even over large areas. This makes modern industries more responsive and reliable.
How Wireless Telemetry Works: Core Components and Data Flow
Wireless telemetry depends on a system of sensors, transmitters, and receivers to collect and transmit data efficiently. Wireless telemetry equipment collects data from machines, environments, and assets, while embedded wireless telemetry ensures smooth sensor-to-cloud communication. Data flows through telemetry data transfer systems to control centers, enabling real-time data streaming and autonomous telemetry tracking. This forms a complete end-to-end telemetry workflow, combining data collection, transmission, analysis, and reporting for modern industrial and commercial operations.
Sensors
Sensors capture data from machines, the environment, or remote assets. They are the first step in the wireless telemetry workflow, enabling accurate and timely monitoring.
Transmitters
Transmitters send collected data from sensors to gateways or control centers. They support device-to-gateway communication and ensure secure wireless transmission.
Receivers
Receivers collect incoming telemetry data and make it available for cloud telemetry analytics. They allow operators to monitor performance and detect anomalies in real time.
Embedded Wireless Telemetry
Embedded telemetry in sensors enables continuous sensor-to-cloud communication. It improves efficiency, accuracy, and reliability in remote and industrial applications.
Key Technologies Powering Modern Wireless Telemetry Systems
Modern wireless telemetry relies on advanced technologies to ensure reliable, real-time data monitoring. Wireless communication modules and data transmission protocols allow seamless remote data transmission from sensors to control centers. Low-power telemetry devices extend operation time, while high-frequency data transfer ensures near-instant updates. Combined with secure wireless transmission and multi-sensor telemetry integration, these technologies provide a robust telemetry architecture for modern industries.
Wireless Communication Modules
These modules enable sensors to send data efficiently over short and long distances. They are essential for autonomous telemetry tracking and maintaining connectivity in industrial environments.
Low-Power Telemetry Devices
Devices designed to consume minimal energy extend system uptime. They reduce maintenance costs and are ideal for remote or hard-to-access locations.
High-Frequency Data Transfer
Frequent updates allow real-time monitoring and quick decision-making. This is crucial for real-time data streaming and cloud telemetry analytics applications.
IoT Connectivity Standards
Standards ensure all devices can communicate smoothly. They support sensor-to-cloud communication and maintain a reliable end-to-end telemetry workflow across multiple platforms.
Major Applications of Wireless Telemetry Across Industries
Wireless telemetry has become a vital tool across multiple industries. Wireless data monitoring allows businesses to track systems and assets remotely, improving efficiency and reducing risks. From healthcare to agriculture, telemetry devices and industrial wireless telemetry provide real-time insights, enabling faster decisions and better outcomes. Wireless data acquisition and remote telemetry systems form the backbone for modern monitoring and management in every sector.
Healthcare Applications
Hospitals use wireless data monitoring to track patient vitals remotely. Doctors receive alerts for irregular readings, improving response times and patient care. Telemetry enables continuous monitoring without needing patients to stay in the hospital.
Manufacturing Applications
Factories rely on industrial wireless telemetry for predictive maintenance and machine monitoring. Wireless automation monitoring detects issues early, reduces downtime, and improves overall productivity.
Energy and Utilities
Energy companies use cellular telemetry systems to monitor grids, substations, and renewable energy installations. Remote telemetry systems provide real-time insights into performance and potential faults.
Agriculture and Environmental Monitoring
Digital telemetry systems in agriculture track soil moisture, irrigation, and livestock health. Wireless environmental monitoring tracks air quality, water levels, and weather, helping farms optimise resources.
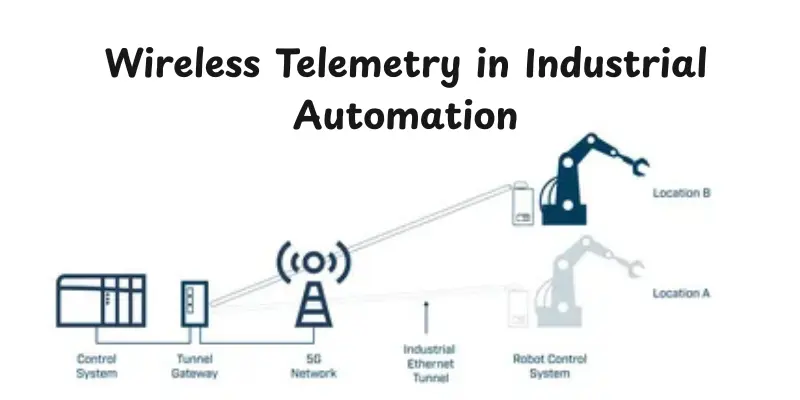
Wireless Telemetry in Industrial Automation and Smart Manufacturing
Modern factories rely on industrial wireless telemetry to efficiently track machines, conveyor belts, and production lines. Wireless machine monitoring allows operators to detect issues early, reducing downtime and cutting maintenance costs. By combining real-time wireless monitoring with telemetry solutions, factories can boost productivity and maintain consistent, smooth operations.
Wireless Telemetry Technology in Factories
Factories use wireless telemetry technology to collect data from sensors on machines and equipment. This technology enables instant alerts when something goes wrong, helping teams respond quickly.
Cloud Telemetry Analytics
Integrating cloud telemetry analytics allows managers to analyze machine performance trends remotely. It supports proactive maintenance and long-term production planning.
Automated Data Reporting
Automated data reporting ensures that factory managers receive performance updates and anomaly alerts without manual intervention. This reduces errors and saves time.
Multi-Sensor Telemetry Integration
Multi-sensor telemetry integration enables simultaneous monitoring of several machines. This provides a complete overview of the factory floor and improves operational efficiency.
Wireless Telemetry in Healthcare and Remote Patient Monitoring
Wireless telemetry in healthcare allows doctors to monitor patients outside hospitals. Wireless IoT telemetry tracks heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels in real time. Telemetry devices securely send sensor-to-cloud data to medical staff. Remote data transmission ensures immediate intervention if vital signs drop.
Hospitals use embedded wireless telemetry and secure wireless transmission to protect sensitive data. Automated data reporting provides real-time dashboards for nurses and doctors. An end-to-end telemetry workflow enables hospitals to manage multiple patients efficiently. Wireless telemetry improves patient safety and reduces unnecessary hospital visits.

Wireless Telemetry in Transportation, Fleet Management, and Logistics
Fleet operators increasingly rely on remote asset tracking telemetry to monitor vehicles, cargo, and overall fleet performance. Wireless telemetry equipment enables real-time data streaming, giving managers instant insights into location, fuel usage, and driver behavior. By using device-to-gateway communication and autonomous telemetry tracking, businesses can avoid delays, prevent accidents, and make smarter decisions for their logistics operations.
- High-frequency data transfer enables continuous fleet status updates, enabling timely action.
- Telemetry communication networks reliably connect vehicles to central monitoring systems.
- Wireless signal relay extends coverage for long-distance trucks and remote areas.
- Cloud telemetry analytics helps predict potential issues and optimize fleet efficiency.
By integrating these advanced systems, logistics companies can improve efficiency, reduce fuel costs, and maintain safe, reliable operations across their fleets. Wireless data monitoring ensures managers always have accurate, up-to-date information.
IoT, Cloud Computing, and Edge Devices in Wireless Telemetry
Wireless telemetry has become a core part of modern industries, especially when combined with IoT and cloud platforms. IoT connectivity standards enable devices to communicate smoothly, while cloud-based telemetry analytics collects and processes wireless sensor data to enable fast, real-time decision-making. Embedded wireless telemetry ensures continuous remote data transmission, giving businesses reliable insights. By integrating edge devices, companies can process data locally, reduce network load, and create an end-to-end telemetry workflow that combines on-site processing with cloud analysis.
IoT Connectivity Standards for Wireless Telemetry
IoT standards allow wireless telemetry devices to communicate seamlessly. Protocols ensure data moves reliably across networks and supports large-scale industrial applications.
Cloud Telemetry Analytics for Real-Time Insights
Cloud telemetry analytics processes wireless sensor data instantly. Businesses can spot trends, detect anomalies, and make decisions quickly without waiting for manual reporting.
Edge Devices and Local Data Processing
Edge devices handle data close to the source. This reduces latency, eases network load, and ensures real-time data streaming for critical industrial operations.
End-to-End Telemetry Workflow Integration
Combining local processing with cloud analytics forms an end-to-end telemetry workflow. Companies can monitor operations effectively using telemetry architecture, low-power telemetry devices, and wireless data acquisition.
Challenges, Limitations, and security Risks in Wireless Telemetry
Wireless telemetry is a powerful tool, but it faces several challenges that industries must address to ensure smooth operations. Issues like interference, latency, and security risks can affect the reliability of real-time data monitoring. Companies need to implement effective strategies to maintain secure wireless transmission and ensure that low-power telemetry devices operate efficiently even in harsh industrial conditions. Proper planning and robust systems are essential for maintaining accurate and timely telemetry data across complex setups.
- Network latency management ensures that real-time wireless monitoring remains accurate and responsive.
- Telemetry devices must be durable and reliable for extreme or remote industrial environments.
- Data transmission protocols and device-to-gateway communication require standardization for smooth integration.
- Companies must secure telemetry data transfer systems and cloud telemetry analytics against cyber threats.
By addressing these challenges, businesses can optimize the performance of their remote telemetry systems and maintain continuous, reliable operations. Regular audits, maintenance, and proper system design improve efficiency and reduce downtime, ensuring that wireless telemetry remains a valuable tool for modern industries.
Future Trends Shaping the Evolution of Wireless Telemetry
Wireless telemetry will integrate more AI, edge computing, and 5G networks. Autonomous telemetry tracking and high-frequency data transfer will provide faster insights. Cloud telemetry analytics will improve predictions in manufacturing, energy, and healthcare. Multi-sensor telemetry integration will enable richer real-time data collection.
Sustainable solutions using low-power telemetry devices are gaining traction. IoT connectivity standards and secure wireless transmission will enhance interoperability and safety. Embedded wireless telemetry will continue to expand into new industries. The future promises smarter, faster, and safer operations through advanced wireless telemetry systems.
Frequently Asked Questions about Wireless Telemetry
Find answers to the most common questions about wireless telemetry and how it works.
Wireless telemetry is used to monitor machines, vehicles, environmental conditions, and assets remotely. It sends real-time data to control centers or cloud platforms. This helps businesses improve efficiency, safety, and decision-making.
Sensors collect data and send it via wireless communication modules to a receiver or cloud system. The data can be analyzed instantly for insights or alerts. This eliminates manual monitoring and speeds up response times.
Healthcare, manufacturing, energy, agriculture, and transportation extensively use wireless telemetry. Hospitals track patient vitals, factories monitor equipment, and farms manage soil and irrigation. Fleet managers and utility companies also rely on it for real-time tracking.
It provides real-time wireless monitoring, remote access, and automated reporting. Businesses can prevent downtime, reduce errors, and optimize resources. It also enables scalable solutions for both small and large operations.
Yes, modern systems use secure wireless transmission and encryption. Only authorized devices can send or receive data. Regular monitoring of telemetry communication networks ensures protection against cyber threats.
Yes, wireless telemetry is scalable and flexible. Small farms, workshops, or fleets can use it without complex infrastructure. It provides wireless sensor data and monitoring solutions that fit any size operation.
Technologies such as sensor-to-cloud communication, high-frequency data transfer, and embedded wireless telemetry make systems more efficient. Cloud telemetry analytics and IoT connectivity standards enhance real-time monitoring. These ensure accurate, fast, and secure data transfer.
Conclusion
Wireless telemetry is transforming the way industries monitor and manage operations. By enabling real-time wireless monitoring, remote data collection, and efficient telemetry data transfer, businesses can make faster, smarter decisions. From healthcare to manufacturing and transportation, wireless telemetry improves efficiency, safety, and productivity. Integrating cloud telemetry analytics, wireless sensor data, and industrial wireless telemetry ensures operations stay connected and reliable. As technology advances, adopting wireless telemetry systems will continue to give companies a competitive edge, streamline processes, and support data-driven decision-making for a brighter, more connected future.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks